515 읽음
National Guideline for the Field Triage of Injured Patients
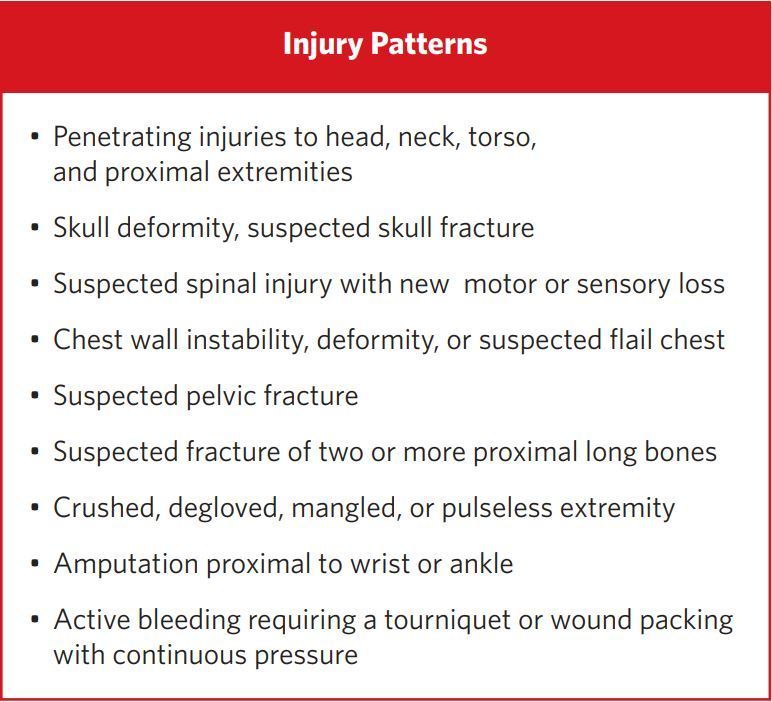
Injury Patterns
• Penetrating injuries to head, neck, torso, and proximal extremities
• Skull deformity, suspected skull fracture
• Suspected spinal injury with new motor or sensory loss
• Chest wall instability, deformity, or suspected flail chest
• Suspected pelvic fracture
• Suspected fracture of two or more proximal long bones
• Crushed, degloved, mangled, or pulseless extremity
• Amputation proximal to wrist or ankle
• Active bleeding requiring a tourniquet or wound packing with continuous pressure
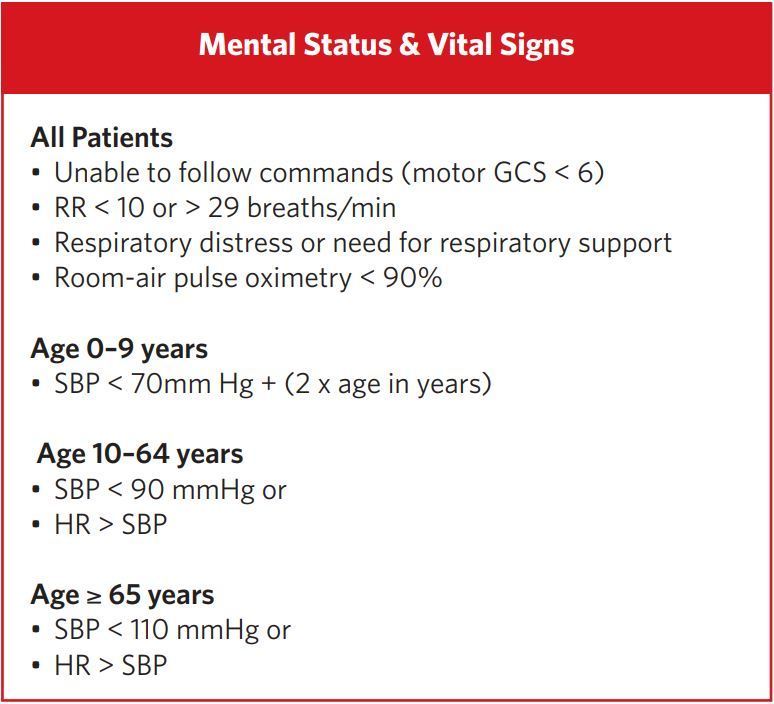
Mental Status & Vital signs
All Patients
• Unable to follow commands (motor GCS < 6)
• RR < 10 or > 29 breaths/min
• Respiratory distress or need for respiratory support
• Room-air pulse oximetry < 90%
Age 0–9 years
• SBP < 70mm Hg + (2 x age in years)
Age 10–64 years
• SBP < 90 mmHg or
• HR > SBP
Age ≥ 65 years
• SBP < 110 mmHg or
• HR > SBP
Patients meeting any one of the above RED criteria should be transported to the highest-level trauma center available within the geographic constraints of the regional trauma system



